How Work Solenoid Valve?
People use solenoid valves to help clean water, make food, work with oil and gas, and run medical machines. Despite their compact size, solenoid valves control complex fluid and gas systems with speed and precision.
This easy-to-follow guide shows you how solenoid valves work, what types you can choose, where people use them, and how you can pick the right one. As a valve maker, we know the problems engineers and buyers face, and what they need from a good valve. This article is your one-stop resource.
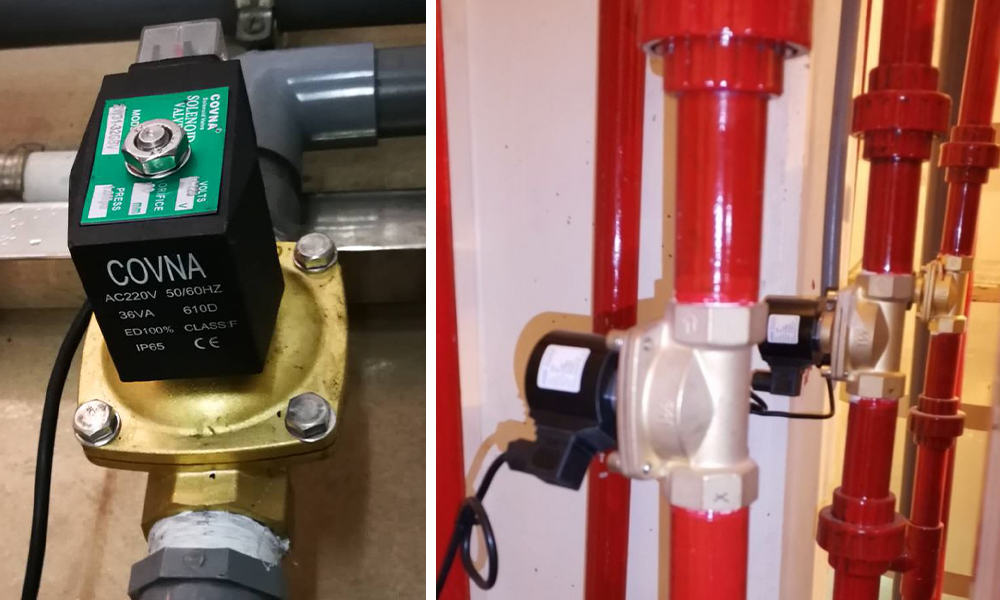

1. What Is a Solenoid Valve?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated valve that controls the flow of liquid or gas. An electric current activates the valve by energizing a coil, which creates a magnetic field. This electromagnetic force moves a plunger, either opening or closing the valve.
Core Function: Convert electrical energy into linear mechanical motion to regulate flow.
Common Uses:
• Turning water supply on/off
• Directing compressed air
• Dispensing chemicals
• Controlling gases in oxygen machines
Solenoid valves help control liquids or gases automatically. They work well when you need to control the flow frequently or from a distance.
2. How Does a Solenoid Valve Work?
The basic principle behind a solenoid valve is the creation of a magnetic field from an electric current. When you apply power, the solenoid (a coil of wire) creates magnetic force that moves a metal plunger or core. This motion either opens or closes the orifice of the valve.
✅ Step-by-Step Working Process:
De-energized state (Normally Closed valve):
• No current → No magnetic field
• Plunger is held in place by a spring
• Valve orifice is closed → No flow
Energized state:
• Electric current flows through the coil
• Magnetic field is generated
• Magnetic field pulls the plunger upward
• Valve orifice opens → Fluid or gas flows
Return to de-energized state:
• Power off → Magnetic field collapses
• Spring pushes the plunger back
• Orifice closes → Flow stops
This simple electromagnetic mechanism enables rapid, repeatable control of flow.
Fun Fact: A solenoid valve can switch in under 50 milliseconds — making them ideal for precise fluid control.
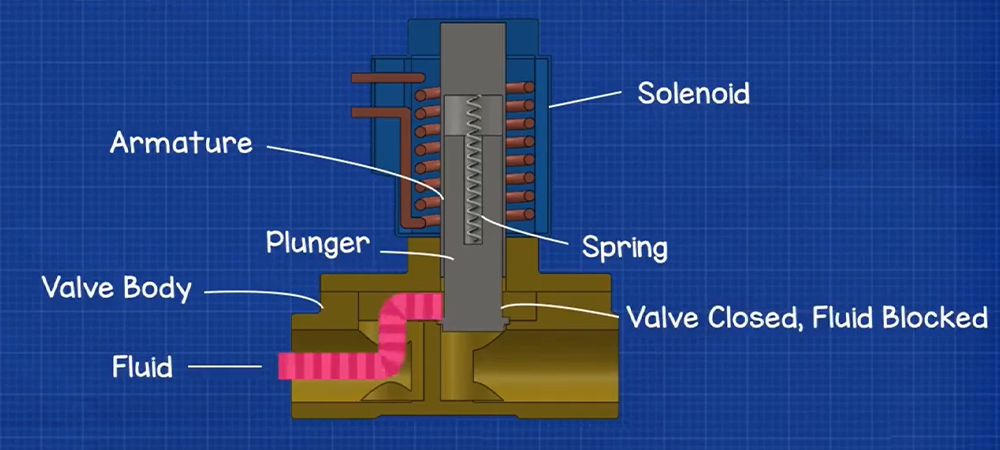
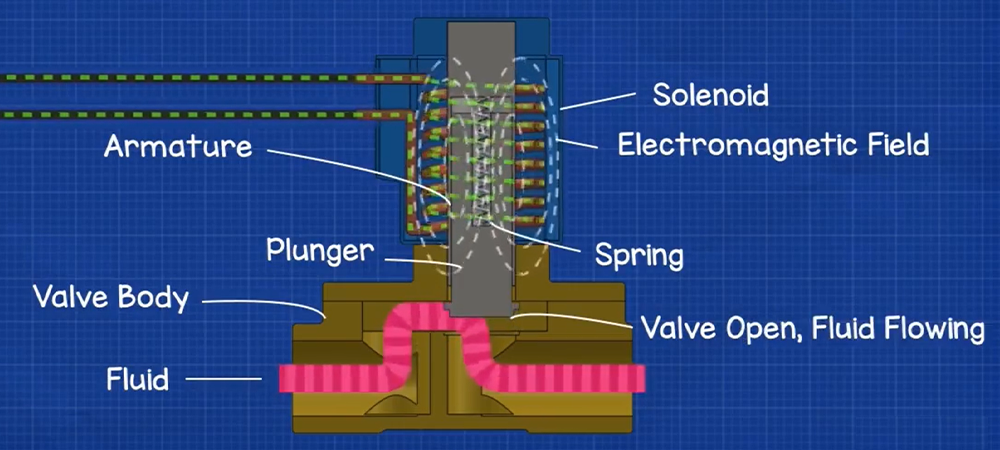
3. Components of a Solenoid Valve
According to RS Online and The Lee Company, a solenoid valve includes the following key parts:
| Component | Function |
| Coil (Solenoid) | Electromagnet that drives movement |
| Plunger (Core/Armature) | Ferromagnetic metal rod moved by the coil |
| Spring | Returns the plunger to its default position |
| Seal/Diaphragm | Prevents leakage; controls flow direction |
| Valve Body | Houses flow channels and ports (brass, stainless steel, or plastic) |
| Orifice | Opening that regulates fluid flow |
Some advanced designs include silencers, pilot channels, orifice seats, and pressure equalization chambers.
4. Types of Solenoid Valves (and How They Work)
Understanding solenoid valve types helps you choose the right configuration for your system.
A. Direct-Acting Solenoid Valve
• Working: The plunger directly opens or closes the orifice.
• Application: Low pressure, small flow systems.
• Speed: Offers rapid response and exceptional reliability.
• Example: Coffee machines and compact pneumatic systems.
B. Pilot-Operated (Indirect) Solenoid Valve
• Working: Uses system pressure to assist valve operation.
• Internal pilot valve opens a small orifice, which then shifts the diaphragm, opening the main valve.
• Application: Large volume and higher-pressure systems.
• Example: Industrial air compression equipment and irrigation system applications.
C. Normally Closed (NC) vs. Normally Open (NO)
-
| Type | Behavior When De-Energized |
| Normally Closed (NC) | Flow is blocked |
| Normally Open (NO) | Flow is allowed |
Choose NC if your system must remain off by default (e.g., fuel shut-off).
Choose NO if flow should continue during a power failure (e.g., emergency cooling).

5. Solenoid Valve Actuation Methods
Solenoid valves are typically electrically actuated, but there are variations:
• Electromechanical: Standard DC/AC-powered solenoid
• Hydraulically assisted: Used in pilot-operated systems
• Pneumatically actuated solenoids: Used for fast switching in compressed air systems
Voltage compatibility includes 12V DC, 24V DC, 110V AC, 220V AC. Always match the valve to your system voltage to avoid coil burnout.
6. Applications of Solenoid Valves
From medical devices to space vehicles, solenoid valves are critical. Here's how they’re used in different sectors:
| Industry | Application | Fluid Type |
| Water & Wastewater | Automated irrigation, flow metering | Water, chlorine |
| Oil & Gas | Remote pipeline control | Natural gas, oil |
| Food & Beverage | Clean-in-place systems | Steam, detergent |
| Pharmaceutical | Sterile liquid dosing | Alcohol, disinfectant |
| Automotive | Fuel injection, exhaust systems | Gasoline, exhaust |
| HVAC | Controlling refrigerant or airflow | Air, R134a gas |
| Medical | Oxygen concentrators, dialysis | Oxygen, saline |
| Semiconductor | Ultra-pure chemical handling | Etchants, DI water |
Solenoid valves are often combined with excess flow valves in safety-critical systems to prevent overload.
7. Materials Used in Solenoid Valves
Choosing the right valve material ensures durability and safety.
| Material | Best For |
| Brass | General use with water, air, neutral gases |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive fluids, high-pressure systems |
| Plastic (Nylon, PVDF) | Chemical resistance, cost savings |
| PTFE/EPDM seals | Chemical and temperature tolerance |
Valve manufacturers like us offer material customization based on your fluid type, pressure, and temperature ranges.
8. Advantages of Using Solenoid Valves
The Engineering Mindset, solenoid valves offer:
Many systems are replacing mechanical valves with solenoids to benefit from precision and automation.

9. Troubleshooting Solenoid Valves
Common issues include:
• Valve not opening/closing: Check for coil failure, plunger sticking, voltage mismatch.
• Humming or buzzing noise: Resulting from the vibration of the AC coil.
• Overheating: Usually caused by incorrect voltage or damage to the coil.
• Fluid leakage: Damaged seal or diaphragm.
️ Maintenance Tip: Perform regular cleaning of valve seats and orifices. Avoid particles or impurities entering the system.
10. How to Choose the Right Solenoid Valve
Here's a quick checklist:
• ✔️ Fluid type (gas, liquid, corrosive, food-grade)
• ✔️ Pressure and temperature range
• ✔️ Response time requirements
• ✔️ Electrical supply voltage
• ✔️ Orifice size and flow rate
• ✔️ Certifications (FDA, ATEX, CE)
We make many types of solenoid valves to fit your needs — from small, simple ones to strong, pilot-operated models. We support OEMs with CAD drawings, test reports, certifications, and after-sales service.
11. Solenoid Valve vs Other Valve Types
| Valve Type | Actuation | Use Case |
| Solenoid | Electric (on/off) | Automation, fast response |
| Motorized Ball Valve | Electric (gradual control) | HVAC, building systems |
| Pneumatic Valve | Air pressure | Cleanrooms, fast switching |
| Manual Valve | Hand-operated | Basic plumbing, infrequent operation |
Solenoid valves are ideal where quick, frequent, and automated flow control is required.
12. Innovations in Solenoid Valve Technology
Leading manufacturers are pushing innovation boundaries:
• Low-power solenoids for battery-operated devices
• Latching solenoids that stay in position without continuous power
• Micro solenoid valves for medical microfluidics
• 4G/IoT-connected valves for remote control and diagnostics
Our R&D team actively supports industrial clients with custom-developed valve systems, including smart control features.
13. Final Thoughts: Why It Pays to Understand How Solenoid Valves Work
Solenoid valves might seem simple at first glance, but they are precision-engineered components vital to modern industry. Whether you’re improving an irrigation system, building a pneumatic device, or buying valves for medical machines, understanding how solenoid valves work helps you make better choices, design smarter, and avoid costly errors.
14. Ready to Order Industrial-Grade Solenoid Valves?
As an experienced manufacturer of solenoid valves, we supply:
• ✔️ OEM and custom-made solutions
• ✔️ Rapid prototyping and samples
• ✔️ Brass, stainless, and plastic valve bodies
• ✔️ Food-grade, anti-corrosion, high-pressure options
• ✔️ Global certifications (CE, RoHS, ATEX)
Contact us today for technical consultation or download our product catalog. Let’s optimize your flow system together.












